How to Calculate Bad Debt Expenses With the Allowance Method Chron com
Content
This accounting entry allows a company to write off accounts receivable that are uncollectible. If the account has an existing credit balance of $400, the adjusting entry includes a $4,600 debit to bad debts expense and a $4,600 credit to allowance for bad debts. The final point relates to companies with very little exposure to the possibility of bad debts, typically, entities that rarely offer credit to its customers. The result of your calculation is what you’ll record on the accounts receivable balance sheet. The adjustment value is the difference between the ending AFDA balance and the starting AFDA balance. Bad debt expense is a natural part of any business that extends credit to its customers.
According to the IRS, an unpaid invoice can only be written off as a bad debt when there isn't a chance the amount due will be paid. In order to do that, you have to be able to demonstrate you’ve taken reasonable steps to collect the debt. If your https://kelleysbookkeeping.com/ client agrees to an invoice, it is recorded by your company right away as an income - regardless of whether it has actually been paid or not. As a rule, the longer it hasn’t been paid, the slimmer the chances of an invoice ever getting paid.
What are the methods used to estimated bad debt under the allowance method?
For example, you’d put 1% bad debt to your 0 to 30 days category, and 30% past 90 days. For example, if a lender's bad debt represented 2% of its total loans last year, and the economy has significantly improved since then, it may only decide to set aside a bad debt reserve of 1.5% of its total loans this year. The alternative is called the allowance method, which is widely used, especially in the financial industry. Basically, this method anticipates that some of the debt will be uncollectable and attempts to account for this right away. Net receivables are the money owed to a company by its customers minus the money owed that will likely never be paid, often expressed as a percentage. When you decide to write off an account, debit allowance for doubtful accounts and credit the corresponding receivables account.
Automating these tasks frees your AR team to focus on executing more strategic, value-added work. Team members can focus their attention on uncovering the causes of payment delays and working with customers to better understand their needs. It creates greater efficiencies, accelerates cash flow, and drastically improves the customer experience. It’s also worth noting that your historical percentage of collections will likely vary between bullish and bearish economic cycles. If your company has enough business history to reference how collections performed in different economic cycles, this can be helpful for casting predictions. When the billing and payment experience isn’t optimized, overall customer experience suffers.
Bad Debt Expense: Definition and How to Calculate It
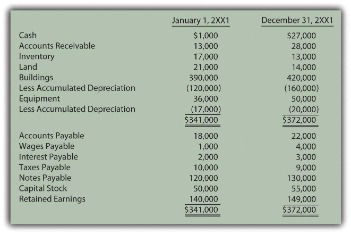
The allowance for doubtful accounts is then used to approximate the percentage of “uncollectible” accounts receivable (A/R). We are balancing the matching principle and usefulness against perfection. We need to provide a reasonable picture of the company’s financial position at the end of the year, and that includes an estimate of accounts that will never materialize into cash. Notice how the subsidiary ledger agrees to the GL control account and does not include our estimated $10,000 of bad debt.
Now let’s imagine that sometime later, a client tells you they won’t be able to pay the $2,000 they owe you. You’ve offered solutions, even a repayment plan, but they won’t budge. It’s a great way to visualize where your accounts receivable are piling up. You can then attribute a percentage of bad debt to each of these categories. Another way to know how much to plan for your bad debt reserve is to use the aging method. The write-off method is the most straightforward way to calculate and report your bad debt.
Allowance Method For Uncollectibles
Because the company may not actually receive all accounts receivable amounts, Accounting rules requires a company to estimate the amount it may not be able to collect. This amount must then be recorded as a reduction against net income because, even though revenue had been booked, it never materialized into cash. The allowance method creates a contra asset allowance account that reduces the net amount of accounts receivable. In order to comply with the matching principle, bad debt expense must be estimated using the allowance method in the same period in which the sale occurs. The allowance method is based on the matching principle in accounting, so it affirms that financial statements have been made using generally accepted accounting principles. Most of its sales happen on credit with an estimated recovery period of 15 days.
- For instance, Customer A might routinely clear 100% of bills within days, but Customer B might have a tendency to default.
- While making it easy for clients to pay you entails enticing payment terms, it’s not the end-all-be-all when it comes to accounts receivable.
- Otherwise, it could be misleading to investors who might falsely assume the entire A/R balance recorded will eventually be received in cash (i.e. bad debt expense acts as a “cushion” for losses).
- For example, based on previous experience, a company may expect that 3% of net sales are not collectible.
Unlike the sales approach, the balance in the allowance account is always adjusted to reflect its current percentage of the accounts receivable balance. If the balance in the allowance account had been $2,000 before the entry, only $4,250 would have been needed for the How To Calculate Bad Debt Expenses With The Allowance Method adjusting entry. As of January 1, 2018, GAAP requires a change in how health-care entities record bad debt expense. Before this change, these entities would record revenues for billed services, even if they did not expect to collect any payment from the patient.
Resources
Instead of sifting through multiple email threads, AR staff and customers alike can find all the information they need in one place. Get instant access to video lessons taught by experienced investment bankers. Learn financial statement modeling, DCF, M&A, LBO, Comps and Excel shortcuts. Based on the GAAP , accrual accounting records transactions when they are rendered.
